In this article, I will briefly explain how to create your own image using Dockerfile. For example, I will be creating an FIO image. FIO is a storage stress test tool and this image can be used for container storage IO benchmarking/ testing.
- Login to the CentOS docker host.
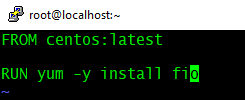
- Create a file named "Dockerfile".
- # vi Dockerfile
- Add the below two lines and save it.
- Once the build is complete, it returns the IMAGE ID as shown below.
- You can use the "docker tag" command to mention a repository and tag to the image.
- At this stage, as shown in the above screenshot, the FIO image is created with repository "vineethac/fio_image" and tagged as "latest".
- You can run this image as given below.
- # docker run -dit --name FIO_test01 --mount source=disk_data,target=/vol vineethac/fio_image fio --name=RandomReadTest1 --readwrite=randread --rwmixwrite=0 --bs=4k --invalidate=1 --direct=1 --filename=/vol/newfile --size=10g --time_based --runtime=300 --ioengine=libaio --numjobs=2 --iodepth=1 --norandommap --randrepeat=0 --exitall
- The above command will start a container with FIO application running inside it. FIO will use "/vol/newfile" for IO tests. "/vol" is using "disk_data" directory which is inside "/var/lib/docker/volumes". Once the test is complete, the container will exit.
Hope it was useful. Cheers!


No comments:
Post a Comment