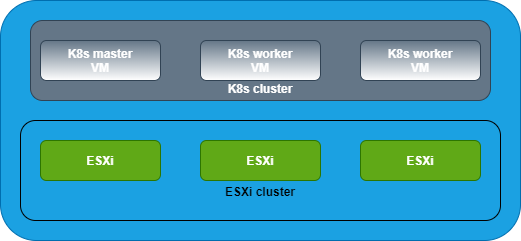
Deploy 3 CentOS 7 VMs. One will be the master and the other two will be workers/ slaves.
Master is "m1" and workers are "w1" and "w2".
Plan IP address
192.168.105.100 - m1
192.168.105.101 - w1
192.168.105.102 - w2
192.168.105.101 - w1
192.168.105.102 - w2
Step1: on all 3 nodes
vi /etc/hosts
192.168.105.100 m1
192.168.105.101 w1
192.168.105.102 w2
192.168.105.101 w1
192.168.105.102 w2
Step2: on all 3 nodes
#Disable firewall
sudo firewall-cmd --state
sudo systemctl stop firewalld
sudo systemctl disable firewalld
sudo systemctl status firewalld
sudo systemctl stop firewalld
sudo systemctl disable firewalld
sudo systemctl status firewalld
setenforce 0
sed -i --follow-symlinks 's/SELINUX=enforcing/SELINUX=disabled/g' /etc/sysconfig/selinux
sed -i --follow-symlinks 's/SELINUX=enforcing/SELINUX=disabled/g' /etc/sysconfig/selinux
Step3: on all 3 nodes
#Configure iptables for Kubernetes
cat <<EOF > /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1
EOF
sysctl --system
cat <<EOF > /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1
EOF
sysctl --system
Step4: on all 3 nodes
#Disable swap
swapoff -a
vi /etc/fstab (Edit fstab file and comment(#) swap partition)
vi /etc/fstab (Edit fstab file and comment(#) swap partition)
reboot all 3 nodes
Step5: on all 3 nodes
#configure kubernetes repo
cat <<EOF > /etc/yum.repos.d/kubernetes.repo
[kubernetes]
name=Kubernetes
enabled=1
gpgcheck=1
repo_gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=https://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/doc/yum-key.gpg https://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/doc/rpm-package-key.gpg
EOF
Step6: Install docker on all 3 nodes
yum install docker -y
Step7: on all 3 nodes
yum install -y kubeadm kubectl kubelet --disableexcludes=kubernetes
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl restart docker && systemctl enable --now docker
systemctl restart kubelet && systemctl enable --now kubelet
systemctl restart docker && systemctl enable --now docker
systemctl restart kubelet && systemctl enable --now kubelet
Step8: on master
kubeadm init --pod-network-cidr 10.244.0.0/16
Step9: on master
$ mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
$ sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
$ sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
Step10: on master
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/coreos/flannel/master/Documentation/kube-flannel.yml
Step11: on all worker nodes
Use the join token from master to join worker nodes to the K8s cluster.
Example:
kubeadm join 192.168.105.100:6443 --token 4j1cjv.gcj2hx9suq5akc7v \
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:b2ead930d772d8af2e45ca8c86c3895b092484c10f8034e52f917e71dc4c3fea
Hope it was useful. Cheers!